Why You're Receiving Mailer Daemon Messages & How to Fix
Arnav Jalan
email security, email error
Mar 1, 2025
Why You're Receiving Mailer Daemon Messages & How to Fix
A mailer daemon message means your email did not get delivered. The recipient's mail server (or your own) rejected it and sent back an automated notice explaining why.
These messages look scary but they are actually helpful. They tell you exactly what went wrong so you can fix it.
What Is a Mailer Daemon?
A mailer daemon is a program that runs on email servers. Its job is to route emails from sender to recipient. When something goes wrong and an email cannot be delivered, the daemon sends a bounce message back to you.
The word "daemon" comes from computing, not mythology. It refers to any background process that runs automatically without user input. Your mail daemon handles delivery behind the scenes. You only hear from it when there is a problem.
These bounce messages come from addresses like:
The message usually includes an error code and a short explanation. Sometimes there is an attachment with technical details.
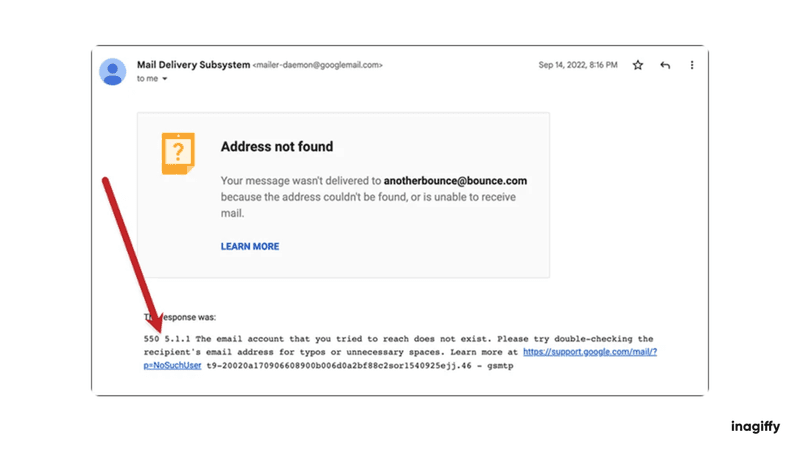
Why Did Your Email Bounce?
There are six main reasons you get mailer daemon messages.
Reason | What Happened | Temporary or Permanent
Invalid address | Email address does not exist | Permanent
Full mailbox | Recipient's inbox is out of space | Temporary
Server down | Recipient's mail server is offline | Temporary
Message too large | Your email exceeds size limits | Permanent (for that message)
Blocked by filters | Spam filters rejected your email | Depends on reason
Spoofing | Someone used your address to send spam | Not your email at all
Let me break these down.
1. The Email Address Does Not Exist
This is the most common reason. You typed the address wrong, or the account was deleted, or the domain no longer exists.
Check for:
Typos (gmial.com instead of gmail.com)
Old addresses that got deactivated
Company domain changes after mergers or rebrands
2. The Mailbox Is Full
The recipient hit their storage limit. Your email cannot fit until they delete something.
This usually fixes itself. Wait a day and try again. If it keeps bouncing, contact them another way and let them know their inbox is full.
3. The Mail Server Is Down
Servers go offline for maintenance, outages, or technical problems. Your email gets stuck in a queue or bounces back.
Temporary issue. Wait a few hours and resend.
4. Your Message Is Too Large
Most email servers cap message size between 10MB and 25MB. If your attachments push you over the limit, the whole email bounces.
Solutions:
Compress your files
Use Google Drive, Dropbox, or WeTransfer instead of attachments
Split into multiple smaller emails
5. Spam Filters Blocked You
The recipient's server decided your email looks like spam. This happens when:
Your content triggers spam filters
Your domain or IP is on a blacklist
You lack proper email authentication (SPF, DKIM, DMARC)
You sent too many emails too fast
If you are running into spam filter issues regularly, read our guide on why emails end up in spam and how to avoid spam filters.
6. Your Address Was Spoofed
If you are getting bounce messages for emails you never sent, someone is using your address to send spam. The spam bounces and the bounce messages come to you.
This does not mean your account was hacked. Spoofing uses your address as a fake "from" field without accessing your actual account.
Soft Bounce vs Hard Bounce
Not all bounces are equal.
Soft bounces are temporary. The email might go through if you try again later.
Examples:
Mailbox full
Server temporarily unavailable
Message size exceeded (for servers with variable limits)
Too many connections to the server
Hard bounces are permanent. The email will never go through to that address.
Examples:
Email address does not exist
Domain does not exist
Recipient blocked your address
Account was deleted
For email marketing, hard bounces matter more. Every hard bounce hurts your sender reputation. Remove hard bounced addresses from your list immediately.
Understanding Error Codes
Mailer daemon messages include error codes. These tell you exactly what went wrong.
4xx Codes (Temporary Problems)
These usually resolve on their own. Try again later.
Code | Meaning
421 | Server not available right now
450 | Mailbox temporarily unavailable
451 | Server error during processing
452 | Not enough storage on server
5xx Codes (Permanent Problems)
These require action from you.
Code | Meaning
550 | Mailbox does not exist or is unavailable
551 | User not on this server
552 | Storage limit exceeded
553 | Mailbox name not allowed
554 | Transaction failed
Extended Codes (X.Y.Z Format)
Some servers use a three-part code for more detail.
First number: 4 = temporary, 5 = permanent
Second number: Category (1 = address, 2 = mailbox, 3 = mail system, 4 = network, 5 = protocol)
Third number: Specific error
Common ones:
Code | Meaning
5.1.1 | Bad destination address
5.1.2 | Bad destination system
5.2.2 | Mailbox full
5.7.1 | Message rejected for policy reasons
4.4.1 | Connection timed out
How to Fix Mailer Daemon Errors
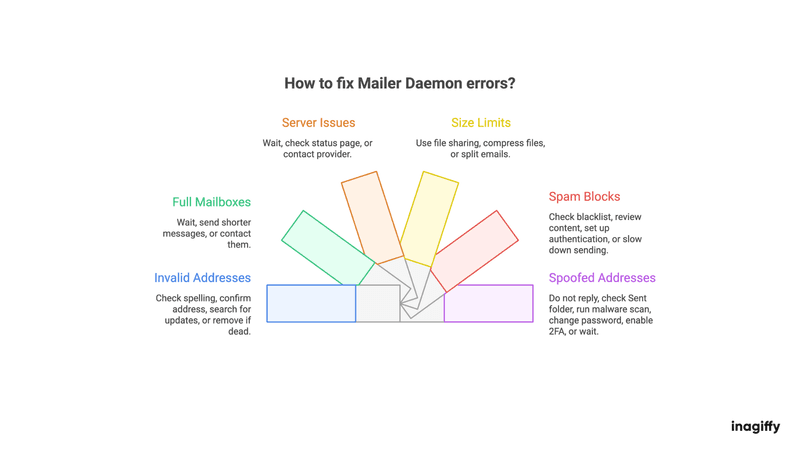
For Invalid Addresses
Check the spelling character by character
Confirm the address through another channel (phone, LinkedIn, website contact form)
Search for updated contact info if the company rebranded
Remove the address from your contacts if it is confirmed dead
For Full Mailboxes
Wait 24 hours and try again
Send a shorter message without attachments
Contact them another way to let them know
For Server Issues
Wait a few hours
Check if the recipient's email provider has a status page
Try again
If it keeps failing, contact your own email provider
For Size Limits
Remove attachments and use file sharing links instead
Compress images and documents
Split your email into multiple smaller messages
For Spam Blocks
This is more complex. You need to figure out why you got flagged.
Check if your domain is blacklisted using MXToolbox
Review your email content for spam trigger words
Make sure you have SPF, DKIM, and DMARC set up correctly
Slow down your sending if you are blasting too many emails
Our email deliverability guide covers this in detail. If authentication is the issue, read about why email authentication fails.
For Spoofed Addresses
Do not reply to the bounce messages
Do not click any links in them
Check your Sent folder to confirm you did not actually send those emails
Run a malware scan just in case
Change your password if you are worried
Enable two-factor authentication
Wait it out (spammers move on after a few days)
Setting up DMARC on your domain can help prevent spoofing in the future.
How to Prevent Bounces
Verify Addresses Before Sending
Use email verification tools before sending to new contacts or importing lists. Services like ZeroBounce, NeverBounce, and Hunter can check if an address is valid before you hit send.
Clean Your Email List Regularly
If you send marketing emails or newsletters:
Remove addresses that bounce twice
Delete inactive subscribers who never open emails
Use double opt-in so people confirm their address
Update your list quarterly at minimum
Stay Under Send Limits
Every email provider limits how many emails you can send per hour and per day. Gmail limits personal accounts to about 500 emails per day. Workspace accounts get 2,000. Going over these limits triggers bounces and can get your account flagged.
If you need to send more, use a proper email marketing platform.
Avoid Spam Triggers
Certain words and patterns make spam filters suspicious:
ALL CAPS in subject lines
Multiple exclamation points!!!
"Free," "Winner," "Urgent," "Act now"
Too many images with little text
Shortened URLs from sketchy services
Missing unsubscribe link (for marketing emails)
For a deeper look at what triggers spam filters, check our guide on staying out of spam traps.
Set Up Email Authentication
Three protocols verify that you are who you say you are:
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) tells receiving servers which mail servers can send email from your domain.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) adds a digital signature to your emails that proves they were not tampered with.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication) tells receiving servers what to do if SPF or DKIM fails.
Setting these up requires access to your domain's DNS settings. If you are not technical, ask your IT team or hosting provider.
Watch Your Sender Reputation
Your sender reputation is like a credit score for email. Good reputation means your emails reach inboxes. Bad reputation means they bounce or land in spam.
Things that hurt your reputation:
High bounce rates
Spam complaints
Sending to purchased lists
Inconsistent sending patterns (nothing for months, then a huge blast)
Things that help:
Low bounce rates
High open and click rates
Engaged subscribers
Consistent sending schedule
What If You Keep Getting Spam Bounces?
If you are flooded with mailer daemon messages for emails you did not send, someone is spoofing your address for a spam campaign.
Do not panic. This happens to everyone eventually. Here is what to do:
Ignore the bounce messages. Do not reply. Do not click links.
Check your Sent folder. If the emails are not there, your account is not compromised.
Run a security scan. Just to be safe.
Change your password. Use a strong one.
Enable two-factor authentication. If you have not already.
Set up DMARC. This tells other servers to reject emails that claim to be from your domain but fail authentication.
Wait. Spammers rotate through addresses. The flood usually stops within a week.
If it does not stop, or if you find suspicious activity in your actual Sent folder, contact your email provider immediately.
FAQs
What does mailer daemon mean?
It means an automated email server program. When you get a message from "mailer daemon," it is the server telling you an email failed to deliver.
Is a mailer daemon message dangerous?
Usually no. It is just a notification that your email bounced. However, if you are receiving bounce messages for emails you never sent, someone may be spoofing your address for spam.
Why do I keep getting mailer daemon messages?
Either you are sending to invalid addresses, your messages are being blocked by spam filters, or your address is being spoofed by spammers. Check your Sent folder to figure out which.
How do I stop mailer daemon emails?
If they are legitimate bounces, fix the underlying issue (wrong address, blocked content, server problem). If they are from spoofed emails you did not send, set up DMARC and wait for the spammers to move on.
What is error code 550?
Error 550 means the mailbox is unavailable. Usually this means the email address does not exist or was deleted.
What is error code 552?
Error 552 means the recipient's mailbox is full or has exceeded its storage limit. Wait and try again later.
Can I reply to a mailer daemon message?
No. Mailer daemon addresses do not accept incoming mail. Replying will just generate another bounce.
How long should I wait before resending after a soft bounce?
Wait at least a few hours for server issues. For full mailboxes, wait 24 hours. If it bounces again, try a different approach.
Quick Reference
Getting bounces for emails you sent:
Check the error code
Fix the issue (address, content, or server)
Clean your list to prevent future bounces
Getting bounces for emails you did not send:
Do not reply or click links
Check that your account is secure
Set up DMARC
Wait for it to stop
Want to improve deliverability overall? Read our email deliverability troubleshooting guide for a complete walkthrough.
Having email deliverability issues? Inagiffy helps businesses build email programs that actually reach inboxes. Learn how we can help.
A mailer daemon message means your email did not get delivered. The recipient's mail server (or your own) rejected it and sent back an automated notice...